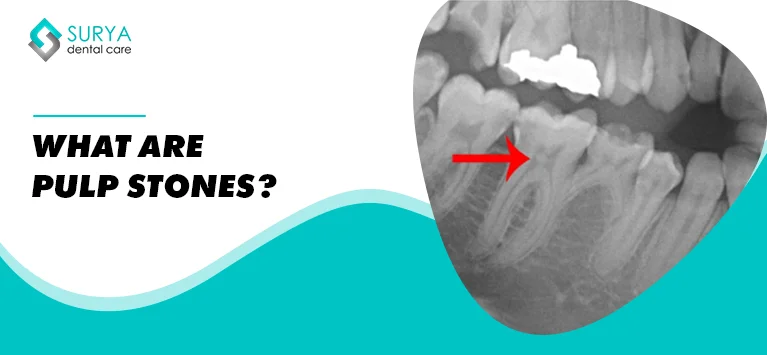
Pulp Stones are typical structures that develop with calcified concentrations in the pulp chamber of your teeth. The pulp is the innermost layer located in the hollow center of a tooth and it holds the nerves, and blood vessels to supply periodontal ligaments with nutrients. The calcifications inside the pulp cavity are hard to detect so they become bigger and are termed Denticles.
In most cases, the pulpal stones are sized between 0.05 mm and 4 mm in diameter. They have a diverse range of possibilities such as they are developed in milk teeth or adult teeth. Similarly, they are found in either the crown region or root portion. Some people have 1 pulp stone in a tooth whereas some people have over 10 pulp stones in a tooth.
Keep reading to know more about this.
How do the pulp stones develop?
The exact cause of this condition is unknown but many dentists believe that the formation of pulp stones begins with the reduction in pulp size due to ageing. Here are the following things that intensify the formation of pulp stones
- When the cells of pulp chamber degenerate and collaborated with minerals, it also leads to the formation of pulp stones.
- The cells in the pulp cavity also lose their density due to ageing so that the cells are lined over the pulp chamber and are followed by calcification that leads to pulpal stones.
- In certain cases, the fat deposits present in the regions around the pulp chamber also tend to Denticles.
- We discovered the pulp stones formed due to the previously treated or restored decayed tooth in some patients. They develop pulp stones due to the fillings with which the tooth was restored.
- People who have pulp stones encounter severe pain in the affected tooth and the stones are hard to detect. Apart from the smaller size, the stones exist in different structures, locations with which they are categorized. So dentists equip radiographs, X-rays, and other advanced imaging systems to identify the stones formed in the pulp cavity.
What are the different types of pulp stones?
As mentioned earlier, pulp stones are classified with factors such as location, size, and structure.
1) Size
- Fine Pulp Stone
- Diffuse Pulp Stone
2) Structure
- True Pulp Stone
- False Pulp Stone
3) Location
- Free pulp stone
- Attached pulp Stone
- Embedded pulp stone
Whatever the size or location where the stone exists, it stimulates intense pain in the problematic tooth and complicates the Endodontic treatments.
How do the pulp stones intervene in Root Canal Treatment?
The root canal procedure involves cleaning and shaping the canals of the root with a needle-like appliance called file. If the pulp stone exists, it will block the path of accessing the canal and make the RCT procedure more challenging.
In most cases, dentists remove the pulp stone through careful instrumentation with the root canal files. In certain cases, a chemical called sodium hypochlorite is utilized to dissolve the stone.
Such a customized approach is mandatory for endodontic treatments because the pulp stones are effective to change the pulp chamber’s anatomy completely. Moreover, the size and structure of the stones are irregular so that they are hard to identify in many cases.
Bottom line
Many people are not aware of the calcified substances developed in our oral cavity. Saliva stones, Tonsil stones, Pulp stones are some calcified structures developed in the oral cavity. Pulp stone is an atypical condition and induces unbearable toothache. Even though it is located in the soft tissue components of a tooth and affects root canal therapy, dentists take care of a customized approach to remove the stone and preserve the tooth.
FAQs
Unless they irritate nerves, most people do not experience discomfort from kidney stones. If left untreated, they can impede the effectiveness of endodontic treatments by obstructing canal access and leading to less than ideal results. Better visualization and seamless instrumentation are facilitated by removal.
Pulp degeneration, aging, circulatory disturbances, cavities, repaired teeth, periodontal illnesses, orthodontic tooth movements, trauma, and genetic predispositions are some of the causes of pulp stones.
The soft tissue in the middle of a tooth is called the pulp, and it contains connective tissue, blood vessels, and nerves that provide the tooth nourishment and feelings.






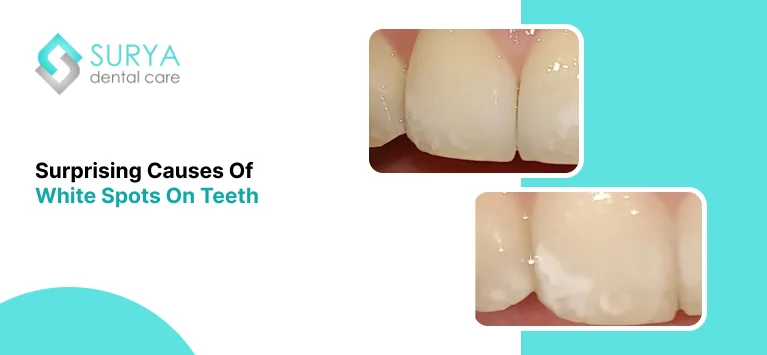







Leave a Comment