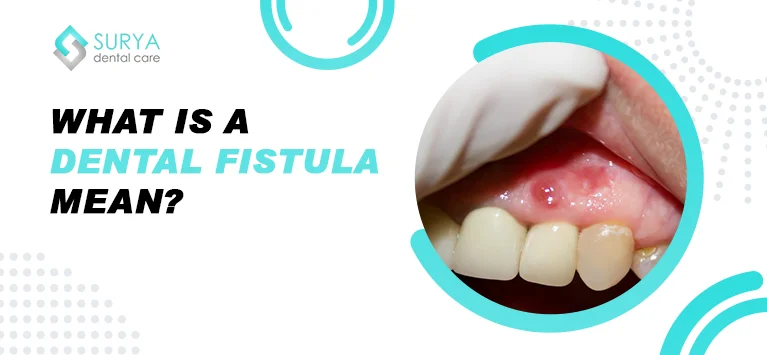
A dental fistula refers to a problematic channel originating from infections inside the mouth, usually in a tooth. It appears like a pimple-like bump on the gums.
In most cases, it begins at the root tip of a tooth and extends to the external surface area of the gums. Thus, an atypical path is created underneath the gums in which a fluid (pus) is deposited. It happens as a secondary effect of some underlying infectious conditions. Hence timely intervention is crucial to treat the root cause of the fistula else the bump will burst out provoking various complications.
What causes an oral fistula?
The fistulae on gums are rooted in various things but mainly in a dental abscess. In general, the fistula begins with the accumulation of white blood cells surrounding the microbes in an infection. It causes swelling or inflammation in the infected site. The pressure applied with swelling detects the area of weakness in the soft or hard tissues inside the oral cavity.
It provides a pathway through which the fluid secreted by the infections gets congregated. Thus a small protuberance called fistula is formed. The most possible causes of dental fistulae include:
- Deep tooth decay
- Infection in gums
- Wisdom teeth
- Poor dental hygiene
- Post-operative complications
In essence, factors that instigate infections inside your mouth are linked to dental fistulae. Fistulas on the gums can also be brought on by inappropriate treatment of cavities and root canal procedures. In certain circumstances, infection in any part of the body might move to the oral cavity causing dental fistulae.
What are the symptoms of dental fistulae?
The dental fistula is not a painful thing but it does cause minor issues that serve as an early warning system for the patient to seek dental care. Here are its common symptoms:
- Tiny bumps on the gums
- Pus discharge in the mouth
- Swollen gums
- Teeth sensitivity
- Large nodes around the neck and jaw
- Pain in teeth that radiates to the ear and neck
How to treat a fistula on gum after root canal?
Beginning with visual assessments, dentists take x-rays of the infected region to detect the root problem hence that the appropriate fistula treatment is prescribed. In most cases, medical procedures to treat the underlying conditions are required to halt the progression and prevent its associated life-threatening complications.
In general, dental doctors might prescribe any or all of the following to treat dental fistulae:
- Antibiotics – Rinsing with antibiotics is the first step to treating the underlying condition of a fistula on gums.
- Extracting the fistula to drain the infected area
- Tooth Extraction
- Root Canal Treatment
How can we prevent dental fistula after treatment?
Proper oral hygiene activities are the key to avoiding subsequent dental fistula. It involves:
- Brushing twice a day
- Flossing to ensure the gaps between teeth are cleaned thoroughly
- Chew sugar-free gums
- Take dairy products
- Consume healthy meals
- Get bi-annual dental check-ups
Takeaway
A dental fistula is a lump filled with pus and it occurs for various reasons. Despite it being painless in most cases, it does not mean it is a benign condition. Dental fistula sufferers are at high risk of developing several life-threatening illnesses.
Hence we recommend getting immediate dental care to address the puss-filled pimple-like bumps on their gums for their wellbeing.
FAQs
A dental fistula usually manifests as a little, pimple-like protrusion or opening on the gum, frequently situated just above the tooth that is afflicted. It might be dripping a tiny bit of pus or fluid, and the gums around it might be swollen and red.
An irregular opening or route that forms in the mouth is called a fistula, and it frequently happens as a result of trauma or illness. It permits pus or other liquids to escape from an internal infection or abscess in the mouth.
Indeed, if left untreated, a dental fistula might pose a threat. Serious consequences may arise if the infection spreads to the jawbone and other regions. Treatment must begin very away in order to stop the infection from getting worse.
An abscess at the tooth's root is typically the cause of an underlying infection indicated by a fistula on the gum tissue above a tooth. It is an unusual tube or aperture that lets pus escape the affected area.





















Leave a Comment