
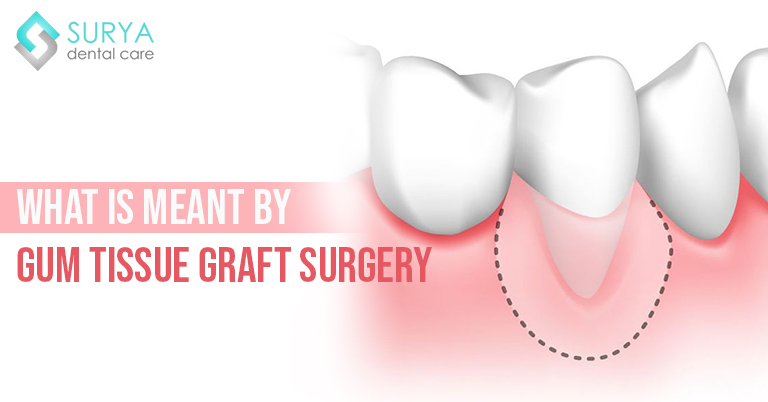
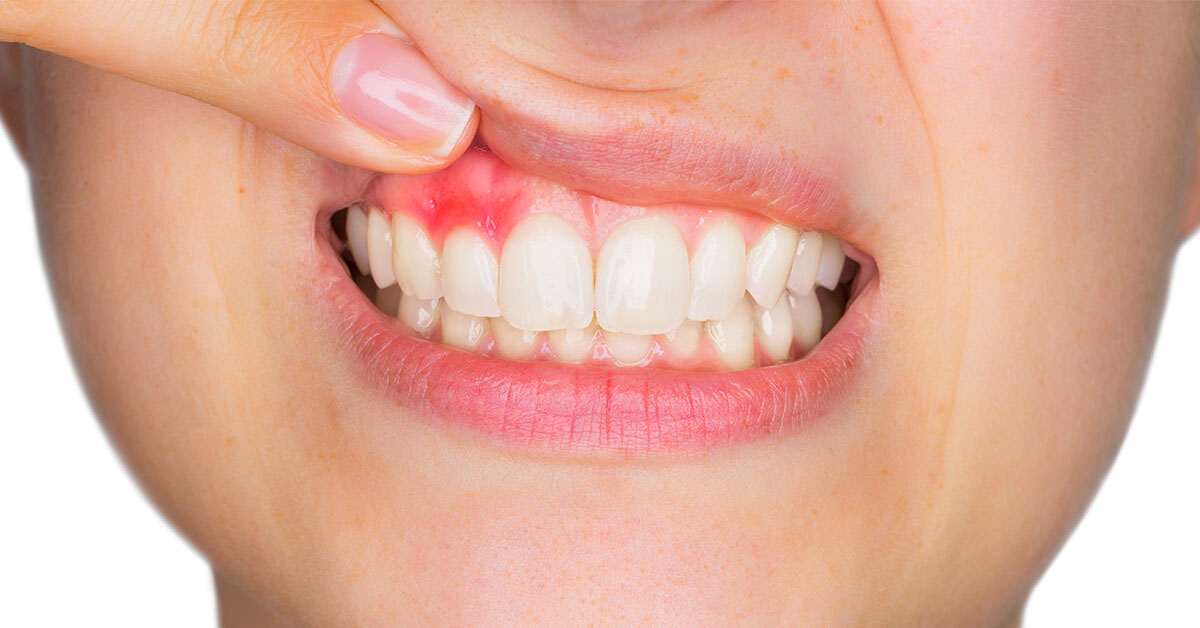
When the gum tissue margins pull away from the teeth, it exposes the tooth roots. Unlike the crown part of a tooth, the root region is not covered with a protective enamel coating. So gum recession will cause sensitivity in teeth in which the surrounding gums have worn away. Meanwhile, the exposed tooth roots are susceptible to plaque build-up and decay.
Such receded gums do not grow back but you can restore the gum tissue surrounding the teeth with a simple surgical procedure called “Gum Graft”.
What is Gum Graft Surgery?
Gum Graft is a quick surgery that involves removing a piece of healthy tissue from the roof of mouth or adjacent gums and attaching them in the region where gums receded.
Gingival graft aims in reversing the detrimental effects of receding gums. In the meantime, it helps in protecting your tooth roots from bacterial attacks and prevents root cavities.
As mentioned earlier, it is relatively a simple procedure and it does not need extensive preparation. So you do not undergo any dietary changes before or on the day of surgery. After the initial consultation followed by a thorough analysis to detect the severity of the recession, your periodontist will recommend the type of gum graft that match your needs.
What are the types of gum graft surgery?
There are 3 types of gum graft surgery. They are:
1) Connective Tissue Graft Surgery – This is the most commonly performed gingival graft procedure. In this method, a flap is made in the palate and connective tissue underneath the top layer is extracted. Now the extracted tissue is stitched to the existing tissues of receded gums.
2) Free Gingival Graft Surgery – It is recommended for people who have thin gums. It also involves extracting the tissues from the roof of the mouth but the difference is, the graft (tissue) is taken directly from the palate’s top layer. It is then grafted onto the area where the gums have worn down.
3) Pedicle Graft Surgery – This is recommended for people who have a lot of gum tissues near the recessed gums. A flap is made in the receding gums or in the gums surrounding the nearby tooth to make grafts. The extracted gum tissues are then stitched to the existing tissues to cover the exposed roots.
- Connective tissue graft
- Free gingival graft
- Pedicle (lateral) graft
What should you do after gum graft surgery?
You can go home shortly after the surgery. Mostly, gingival graft surgery has high success rates whilst the success rates depend on your care during the recovery period.
Our periodontists have recommended the highly prescribed gun graft aftercare instructions for fast healing and avoid possible side effects.
- Take soft and cold foods
- Avoid spicy, hard, and hot cuisines
- Swish your mouth with antimicrobial mouthwash for at least 2 weeks following the surgery
- Don’t smoke and chew tobacco products
- Don’t indulge in strenuous exercises
- Brush and floss gently in sites close to the treated region
- Take antibiotics to avoid infection
Bottom line
Receding gum is a common dental problem but its aftereffects are more harmful than you think. When the tooth roots are exposed due to gum recession, it is followed by bacteria build up on the roots and severely damage the tooth’s bone structures.
Even though the receded gums cannot grow back naturally, you should restore them with gum graft surgery for the tooth’s well-being.












Leave a Comment